Cursor 2.0: A Quantum Leap in AI-Powered Development with Parallel Agent Collaboration
The landscape of software development is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the relentless advancement of artificial intelligence. For years, developers have leveraged AI assistants as powerful copilots, tools that augment their workflow through intelligent code completion, bug detection, and boilerplate generation. However, this partnership has largely been a one-to-one conversation—a single developer interacting with a single AI. This linear approach, while beneficial, has inherent limitations, often mirroring the constraints of a single-threaded process. The true potential of AI lies not just in assistance, but in genuine, scalable collaboration.
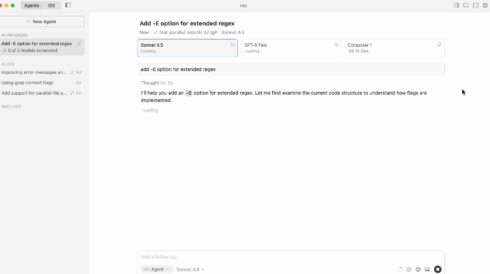
Enter Cursor 2.0, the next evolution of the AI-native code editor. This landmark release isn’t merely an incremental update; it’s a fundamental reimagining of the developer-AI relationship. Cursor 2.0 shatters the single-assistant paradigm by introducing a revolutionary multi-agent interface, allowing up to eight AI agents to work on a codebase simultaneously and in parallel. This innovation is supercharged by the debut of Composer, Cursor’s first proprietary coding model, engineered for speed and deep contextual understanding. By orchestrating a team of AI agents, Cursor 2.0 transforms the developer from a lone coder into the conductor of a high-performance software engineering symphony, poised to tackle complex challenges with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
Redefining the Developer Workflow: The Multi-Agent Interface
The most profound change in Cursor 2.0 is its conceptual pivot from a file-centric to an agent-centric development environment. Traditional IDEs, and even first-generation AI editors, organize work around a tree of files and folders. Cursor 2.0 introduces a new dimension where the primary actors are autonomous agents, each capable of undertaking complex tasks across the entire codebase.
This new interface empowers a developer to deploy up to eight agents in parallel. Imagine you’re building a new feature that requires backend API changes, frontend UI updates, and new database migrations. In a conventional workflow, a developer would tackle these tasks sequentially, context-switching between different parts of the code. With Cursor 2.0, you can assign each of these tasks to a separate agent.
- Agent 1: Refactors the user authentication service in the backend.
- Agent 2: Builds a new React component for the user profile page.
- Agent 3: Writes the SQL script for a new database schema.
- Agent 4: Generates unit tests for the new API endpoints.
These agents execute their tasks concurrently, dramatically compressing the development timeline. The developer’s role evolves from writing every line of code to defining high-level goals, reviewing the agents’ work, and integrating their solutions.
The Technical Foundation of Parallelism
Enabling multiple autonomous agents to modify a single codebase without causing chaos is a significant technical challenge. Cursor 2.0 solves this elegantly by leveraging powerful Git functionalities under the hood.
By using
git worktreesand remote trees, Cursor ensures that each agent operates in an isolated environment. This prevents them from interfering with each other’s work, eliminating the risk of conflicting changes and merge nightmares that would otherwise make parallel development untenable.
A git worktree allows a developer to have multiple working versions of a repository checked out simultaneously. In the context of Cursor 2.0, each agent is assigned its own worktree. This means Agent 1 can be modifying a file on the feature/api branch while Agent 2 works on the same file in a completely separate worktree for the feature/ui branch. These isolated sandboxes are the key to enabling safe, concurrent code modification.
Furthermore, this multi-agent architecture introduces a powerful new method for problem-solving: competitive collaboration. A developer can assign the exact same complex problem to multiple agents, each perhaps powered by a different underlying model (like GPT-4, Claude 3, and Composer). Within moments, you can compare and contrast several distinct solutions, selecting the most efficient, elegant, or performant approach. This transforms a difficult coding challenge from a singular effort into a rapid, multi-pronged exploration of the solution space.
| Feature | Traditional AI Assistant Workflow | Cursor 2.0 Multi-Agent Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Task Handling | Sequential, one task at a time. | Parallel, up to eight tasks simultaneously. |
| Problem Solving | A single AI provides one solution. | Multiple AIs can attempt the same problem, providing diverse solutions for comparison. |
| Codebase Interaction | Can introduce conflicts if not carefully managed. | Agents operate in isolated git worktrees, preventing conflicts by design. |
| Developer Role | Coder, assisted by a copilot. | Architect and reviewer, orchestrating a team of AI agents. |
| Project Velocity | Linear progression. | Exponential acceleration through concurrent execution. |
While this new agent-centric view is the future, Cursor 2.0 provides flexibility. Developers who prefer a traditional approach can still open individual files or switch back to the classic IDE view at any time, ensuring a smooth transition for all users.
Introducing Composer: The Engine Driving Low-Latency Agentic Coding
A revolutionary multi-agent system requires an equally revolutionary engine to power it. Cursor 2.0 introduces Composer, the company’s first-ever proprietary coding model. Composer has been meticulously designed from the ground up to excel at the specific demands of low-latency, agentic coding tasks.
The headline achievement of Composer is its incredible speed. The company claims it is four times faster than similar models, a critical factor for maintaining a developer’s flow state. In agentic workflows, where the AI takes multiple “turns” to reason through a problem, create a plan, and execute it, latency is the enemy of productivity. Composer is engineered to complete most of these turns in under 30 seconds, providing a near real-time conversational experience that keeps momentum high.
Trained for Deep Codebase Understanding
Speed alone is not enough. An effective coding agent must possess a deep and holistic understanding of the entire project it’s working on. To achieve this, Composer was trained on a diverse set of specialized tools, with a particular emphasis on codebase-wide semantic search.
Traditional keyword-based search can find function names or variables, but it lacks true comprehension. Semantic search, in contrast, understands the intent and contextual meaning behind the code. When an agent powered by Composer is asked to “implement a more secure user session handler,” it doesn’t just look for files named session.js. It understands the relationships between user models, authentication middleware, database schemas, and API endpoints. This allows it to:
- Navigate Large Codebases: Intelligently identify all relevant files and dependencies related to a task, even in monolithic repositories with millions of lines of code.
- Respect Existing Patterns: Analyze the project’s architecture and coding conventions to produce new code that is consistent and idiomatic.
- Perform Complex Refactoring: Safely execute codebase-wide changes, understanding the downstream impact of modifying a core function or class.
This deep contextual awareness makes Composer not just a code generator, but a true collaborator that can reason about software architecture at a high level.
A Symphony of Features: Enhancing the End-to-End Development Cycle
Beyond the headline features of the multi-agent interface and the Composer model, Cursor 2.0 is packed with a suite of enhancements designed to streamline every phase of the development lifecycle. These features work in concert to create a cohesive, intelligent, and remarkably efficient coding environment.
Streamlined Code Review and Native Testing
AI-generated code, no matter how advanced, requires human oversight. Cursor 2.0 recognizes this and introduces an improved interface for reviewing the work produced by its agents. This makes it easier for developers to inspect diffs, understand the agent’s reasoning, and provide corrective feedback, ensuring that quality and control remain firmly in the hands of the developer.
Perhaps one of the most significant workflow improvements is the new native browser tool. A common source of friction for developers is the constant context-switching between their code editor and a web browser to test changes. Cursor 2.0 integrates this feedback loop directly into the editor. An agent can now write code, deploy it to a test environment, and observe the results in the integrated browser. If the output isn’t correct, the agent can autonomously iterate on its code, test again, and continue this cycle until the intended result is achieved. This closes the loop between implementation and validation, creating a powerful, self-correcting development process.
Collaboration and User Experience Enhancements
Cursor 2.0 also brings powerful new features for development teams and individual user experience:
- Custom Team Commands: Engineering teams can now create and share custom commands across their organization. This allows them to encapsulate complex, multi-step prompts or enforce specific coding standards. A command like
/apply-internal-logging-standardcan be used by any team member to ensure all new code adheres to company-wide conventions, boosting consistency and collaboration. - Voice Mode: For developers who prefer a more natural, conversational interaction, Cursor 2.0 introduces a new voice mode. This enables hands-free coding and allows for a different modality of interaction, increasing accessibility and catering to diverse workflows.
- Improved Prompt UI: The interface for writing prompts and instructing the AI has been redesigned for greater clarity and power. This helps developers craft more effective instructions, leading to better and more accurate results from the AI agents.
The Practical Implications: How Cursor 2.0 Will Transform Development Teams
The features introduced in Cursor 2.0 are not just theoretical advancements; they have tangible, real-world implications for how software is built. This new paradigm promises to accelerate productivity, enhance code quality, and ultimately reshape the roles of developers and teams.
For the individual developer, the impact is immediate. The ability to delegate multiple tasks to parallel agents dramatically reduces the time spent on tedious, boilerplate, and repetitive coding. A developer can focus their creative energy on the most challenging architectural problems while agents handle the implementation details. This not only speeds up feature development but also reduces cognitive load and burnout, allowing for more sustained periods of deep work.
For the development team, the benefits are compounded. The shared custom commands create a living repository of best practices, accelerating the onboarding of new engineers and ensuring a consistent level of quality across all projects. The ability for agents to understand and work within large, existing codebases means that even complex legacy systems become more manageable and easier to modernize.
For the business, the ultimate result is a significant acceleration in time-to-market. By parallelizing development work that was previously sequential, teams can deliver features and products faster than ever before. This increased velocity allows organizations to respond more quickly to market demands, innovate more rapidly, and gain a decisive competitive edge.
The Future is Collaborative: Looking Beyond Cursor 2.0
Cursor 2.0 represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of AI-powered software development. We are moving beyond the era of AI as a simple autocomplete tool and into a new age of AI as a collaborative partner and force multiplier. The shift from a single copilot to a team of orchestrated agents is a paradigm shift that will have lasting effects on the industry.
This release sets the stage for an even more integrated future. One can imagine a future where AI agents not only write and test code but also participate in the entire DevOps lifecycle—automatically deploying to staging environments, monitoring for performance regressions, and even responding to production incidents. The developer’s role will continue to elevate, becoming more strategic, creative, and focused on guiding these intelligent systems to build the next generation of software.
Cursor 2.0 is more than just a product update; it’s a bold vision for a future where human ingenuity is amplified by the parallel processing power of AI. By providing the tools to conduct this powerful symphony of agents, Cursor is empowering developers to build better software, faster.
For more detailed information on this release, you can review the official announcement available here.






Comments