The Future is Unified: MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 Redefines the Database Landscape
In the modern digital economy, data is the lifeblood of every organization. From the click of a button on an e-commerce site to the complex algorithms powering financial markets, data underpins every transaction, interaction, and decision. However, as the volume and variety of data have exploded, so too has the complexity of managing it. For decades, organizations have been forced to navigate a fragmented landscape of specialized databases, creating a tangled web of systems that hinder innovation and slow progress.
Traditionally, businesses have relied on a siloed approach to data management. Transactional data, the engine of daily operations, lived in one type of database (OLTP). Analytical data, crucial for business intelligence and strategic planning, was shuttled to another (OLAP or a data warehouse). And with the recent meteoric rise of artificial intelligence, a third silo has emerged: the vector database, designed to handle the complex data structures required for AI and machine learning models. This separation creates immense architectural friction, forcing developers and data engineers to build and maintain brittle, expensive data pipelines just to move information between systems.
This is the challenge that MariaDB has set out to solve with its latest, groundbreaking release. MariaDB has announced the Enterprise Platform 2026, a transformative solution poised to act as “the definitive database platform for building next-generation intelligent applications.” This is not merely an incremental update; it is a fundamental rethinking of what a database can and should be. By seamlessly combining transactional, analytical, and vector database capabilities into a single, unified platform, MariaDB is eliminating the silos that have long plagued the industry and paving the way for a new era of intelligent, data-driven applications.
Breaking Down the Silos: The Power of a Truly Unified Database
For years, the conventional wisdom in database architecture was to use the right tool for the right job, even if it meant using many different tools. This led to a standard, albeit cumbersome, setup in most enterprises:
- Transactional Systems (OLTP): Databases like MariaDB’s traditional engine, optimized for fast, high-volume read/write operations like processing orders, updating customer records, and managing inventory.
- Analytical Systems (OLAP): Data warehouses or columnar stores designed to perform complex queries on vast amounts of historical data, powering business intelligence dashboards and reports.
- Vector Databases: A newer category built specifically to store and query high-dimensional vector embeddings, which are essential for AI applications like semantic search, recommendation engines, and generative AI.
While logical in theory, this separation creates a cascade of practical problems. Data must be constantly extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL) from the transactional system to the analytical warehouse, introducing latency that means insights are always based on past data, not real-time information. Introducing AI adds another layer of complexity, requiring yet another data pipeline to feed the vector store. This architectural complexity translates directly into tangible business challenges: delayed decision-making, increased infrastructure and maintenance costs, duplicated data, and a slower pace of innovation.
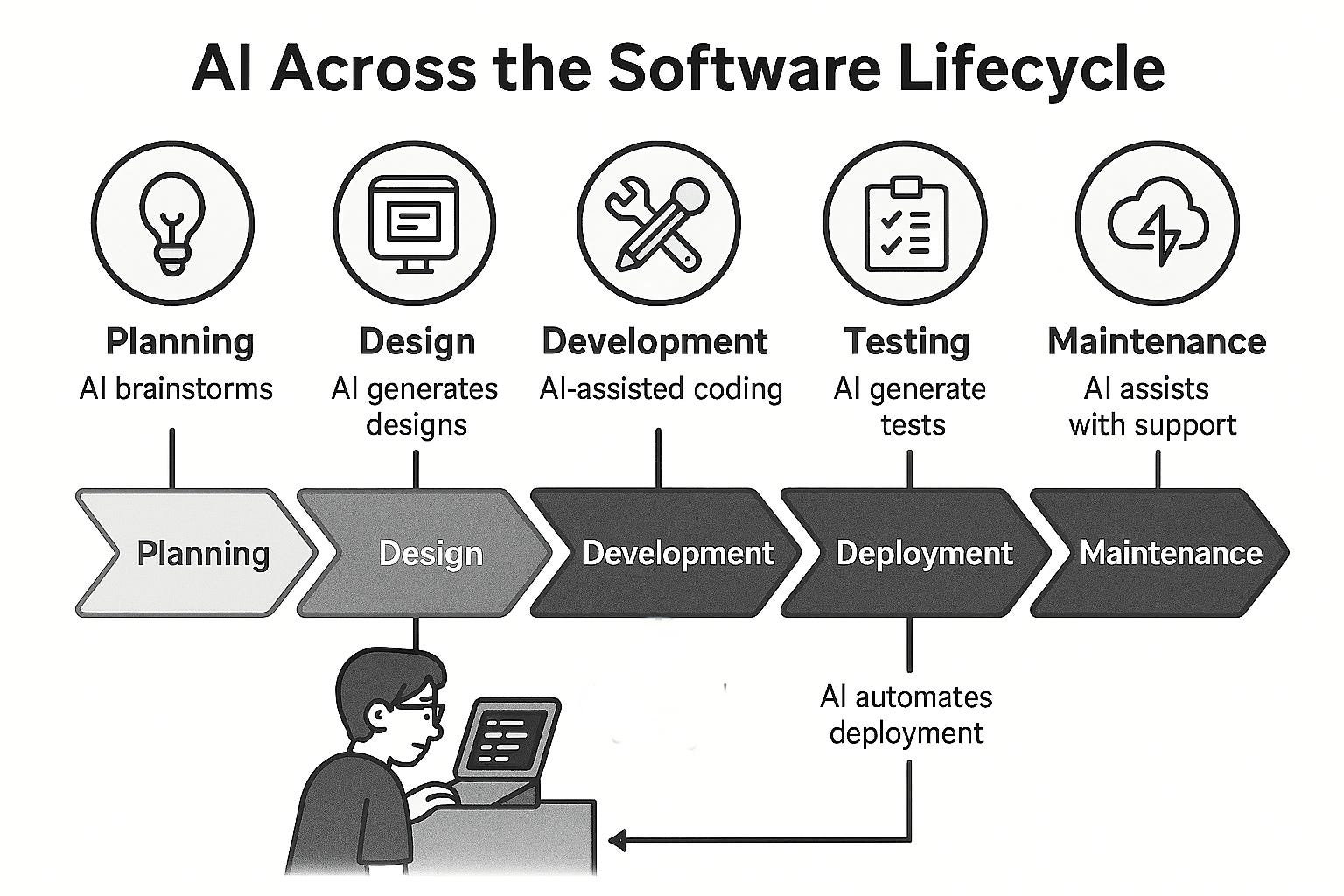
MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 dismantles this outdated paradigm. By integrating these three distinct workloads into one cohesive platform, it offers a radically simplified and more powerful approach. The platform allows businesses to perform complex analytics directly on their live, operational data and to build sophisticated AI features without ever moving that data to a separate system. This convergence unlocks a host of benefits, streamlining operations, reducing total cost of ownership, and, most importantly, empowering organizations to build smarter, more responsive applications.
Fueling the Agentic AI Revolution
The next frontier of artificial intelligence is not just about chatbots or simple automations; it’s about creating “agentic AI”—intelligent, autonomous agents that can reason, plan, and take action to achieve complex goals. These agents need to do more than just retrieve information; they must be able to probe, analyze, and transact with data in real-time and at an immense scale. This requires a database foundation that is both powerful and deeply integrated with AI capabilities. MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 is purpose-built for this future.
To support this new wave of applications, MariaDB has introduced a suite of powerful, AI-native features:
Native RAG for Grounding LLMs: The platform includes native Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a revolutionary feature that allows Large Language Models (LLMs) to be grounded with context directly from the enterprise’s own data. Critically, this is achieved without the need for separate embeddings, external vector stores, or complex retrieval pipelines, dramatically simplifying the process of building accurate and context-aware AI applications.
Ready-to-Use AI Agents: MariaDB is embedding intelligence directly into the platform with pre-built agents designed to augment human capabilities: * Developer Copilot: This agent acts as an intelligent assistant for developers, allowing them to interact with the database using natural language queries. Instead of writing complex SQL, a developer can simply ask, “Show me the top 10 selling products in the European market for the last quarter.” This accelerates development cycles and lowers the barrier to entry for building data-rich applications. * DBA Copilot: This agent is designed to automate and simplify the complex tasks of database administration. It can proactively manage performance tuning, assist with debugging, and handle routine maintenance, freeing up highly skilled DBAs to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Integrated MCP Server: At the heart of this AI ecosystem is an integrated MariaDB Common Purpose (MCP) server. This acts as the central interface for AI agents, allowing them to seamlessly interact with MariaDB databases. The MCP interface unifies vector search, LLMs, and standard SQL operations, giving agents a powerful and flexible toolkit for data interaction. Furthermore, it empowers agents to programmatically launch serverless databases in the cloud, enabling dynamic and scalable application architectures.
Supercharging Analytics: Introducing MariaDB Exa and Enhanced ColumnStore
The ability to analyze data in real time is a critical competitive advantage, yet it has remained elusive for many organizations due to the limitations of traditional architectures. MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 directly addresses this with MariaDB Exa, a formidable new analytics offering designed for multi-terabyte, complex analytics on live operational data.
MariaDB claims this new engine is a staggering 1000x faster than traditional OLTP engines for analytical queries. Its true power, however, lies in its seamless integration. Because Exa runs directly alongside MariaDB’s transactional database, there is no need to move data to a separate system. This eliminates ETL latency, allowing businesses to query and analyze up-to-the-second business data as it is generated.
The following table illustrates the paradigm shift enabled by this integrated approach:
| Feature | Traditional Analytics Approach | MariaDB Exa Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Data Location | Data moved to a separate data warehouse or data lake. | Analytics performed directly on operational data. |
| Data Freshness | Lag due to ETL/ELT processes (batch updates). | Real-time, up-to-the-second insights. |
| Architecture | Complex, multi-system architecture requiring data pipelines. | Simplified, integrated within the MariaDB platform. |
| Query Speed | Dependent on the performance of the separate warehouse. | Up to 1000x faster than traditional OLTP engines for analytics. |
| Maintenance | Requires managing and synchronizing separate systems. | Unified management and maintenance. |
Complementing this is a major update to MariaDB ColumnStore, the platform’s existing columnar storage engine. The new release introduces a powerful query accelerator that can directly process transactional data, enabling parallel OLAP queries on real-time business information. The update also brings new read-replica nodes, allowing organizations to scale compute resources independently without the need to redistribute data. This is further enhanced by integrated cluster management tools, automated upgrade processes, and expanded data import options, making large-scale analytics more accessible and manageable than ever.
Centralized Command and Control: Enhanced Management and Security
A powerful platform is only as good as its ability to be managed and secured. Recognizing this, MariaDB has invested heavily in the operational aspects of the Enterprise Platform 2026.
Key additions include:
- MariaDB Enterprise Manager: This new tool provides a centralized, “single pane of glass” view of the entire database environment. Administrators can monitor performance, manage configurations, and optimize resources across transactional, analytical, and AI workloads from one intuitive dashboard. This holistic visibility simplifies administration, reduces overhead, and helps prevent issues before they impact the business.
- Advanced Database Firewall: Security is paramount, and the new platform introduces a sophisticated database firewall within MariaDB MaxScale, the platform’s advanced database proxy. This firewall provides a critical layer of defense, protecting against threats like SQL injection, controlling data access based on granular policies, and monitoring for suspicious activity in real time.
- General Availability of MariaDB Cloud Serverless: The release also marks the general availability of MariaDB Cloud Serverless. This offering provides a fully managed, auto-scaling database experience that frees developers from the burden of infrastructure management. With a pay-per-use model, it offers a cost-effective and highly elastic solution for applications with variable or unpredictable workloads.
The Vision for the Future: A Platform Built for Intelligent Applications
The MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 is more than just a collection of features; it’s a bold vision for the future of data management. It’s a direct response to the demands of a world where AI is becoming deeply embedded in every application and real-time insights are no longer a luxury but a necessity.
Vikas Mathur, Chief Product Officer of MariaDB, perfectly encapsulates this vision:
“The future of applications is agentic. AI agents need to probe, analyze and transact in real time and at enormous scale. At the same time, agents need to be grounded in insights contained in enterprise data that is trapped in fragmented silos today. MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 is purpose-built to eliminate that architectural friction. In combining transactional, analytical and AI workloads, we are enabling our customers to build the next wave of intelligent applications on a single database platform, shortening the path from raw transactional data to valuable business outcomes.”
This statement highlights the core mission of the platform: to eliminate friction and accelerate value creation. By providing a single, unified foundation for all data workloads, MariaDB is empowering organizations to build the next generation of intelligent systems—applications that can not only process transactions but also understand context, predict outcomes, and take autonomous action.
Conclusion: Embracing a New Era of Data Convergence
The release of MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 marks an inflection point for the database industry. It signals a decisive move away from the fragmented, siloed architectures of the past and toward a future of unified, intelligent data platforms. The convergence of transactional, analytical, and vector workloads is no longer a theoretical ideal but a practical reality.
For businesses looking to innovate and compete in an increasingly AI-driven world, this is a pivotal moment. The ability to harness all of an organization’s data—live and historical, structured and unstructured—within a single, cohesive ecosystem is the key to unlocking transformative outcomes. MariaDB has delivered a platform that not only meets the complex demands of today but is also built to power the intelligent, agentic applications of tomorrow. By breaking down the walls between data silos, MariaDB Enterprise Platform 2026 is not just simplifying database management; it’s shortening the path from raw data to real-world value and ushering in a new era of data convergence.






Comments